C.C.P. Contact Probes Co., LTD.
C.C.P. Contact Probes Co., LTD.
Do you know what a rigid-flex board is? This article will guide you to understand what a rigid-flex board is, its potential applications, and the key features of using a rigid-flex board!
What are the advantages of a Rigid-flex Board?
A Rigid-flex Board (also known as a flexible hybrid circuit) is an innovative product that combines flexible printed circuits (FPC) with rigid printed circuits (PCB). Its inception and development stem from the pursuit of manufacturing cost-effectiveness and application efficiency. Rigid-flex board technology enables the integration of the bendable characteristics of flexible circuits with the stability of rigid circuits. Through processes such as lamination, these two components are seamlessly fused to meet the relevant process requirements. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the definition, application areas, and the advantageous features of Rigid-flex Boards.
What is a Rigid-flex Board?
Rigid-flex Boards, primarily used as alternatives to rigid printed circuit boards (PCBs), offer advantages such as shared blind and buried via designs, as well as the capability for higher circuit density layouts. This design not only possesses the characteristics of rigid boards but also incorporates the advantages of flexible printed circuits (FPC), including being lightweight, thin, and durable. The two rigid boards are interconnected and laminated with the flexible board in between, forming a single printed circuit board, commonly referred to as a Rigid-flex Board.
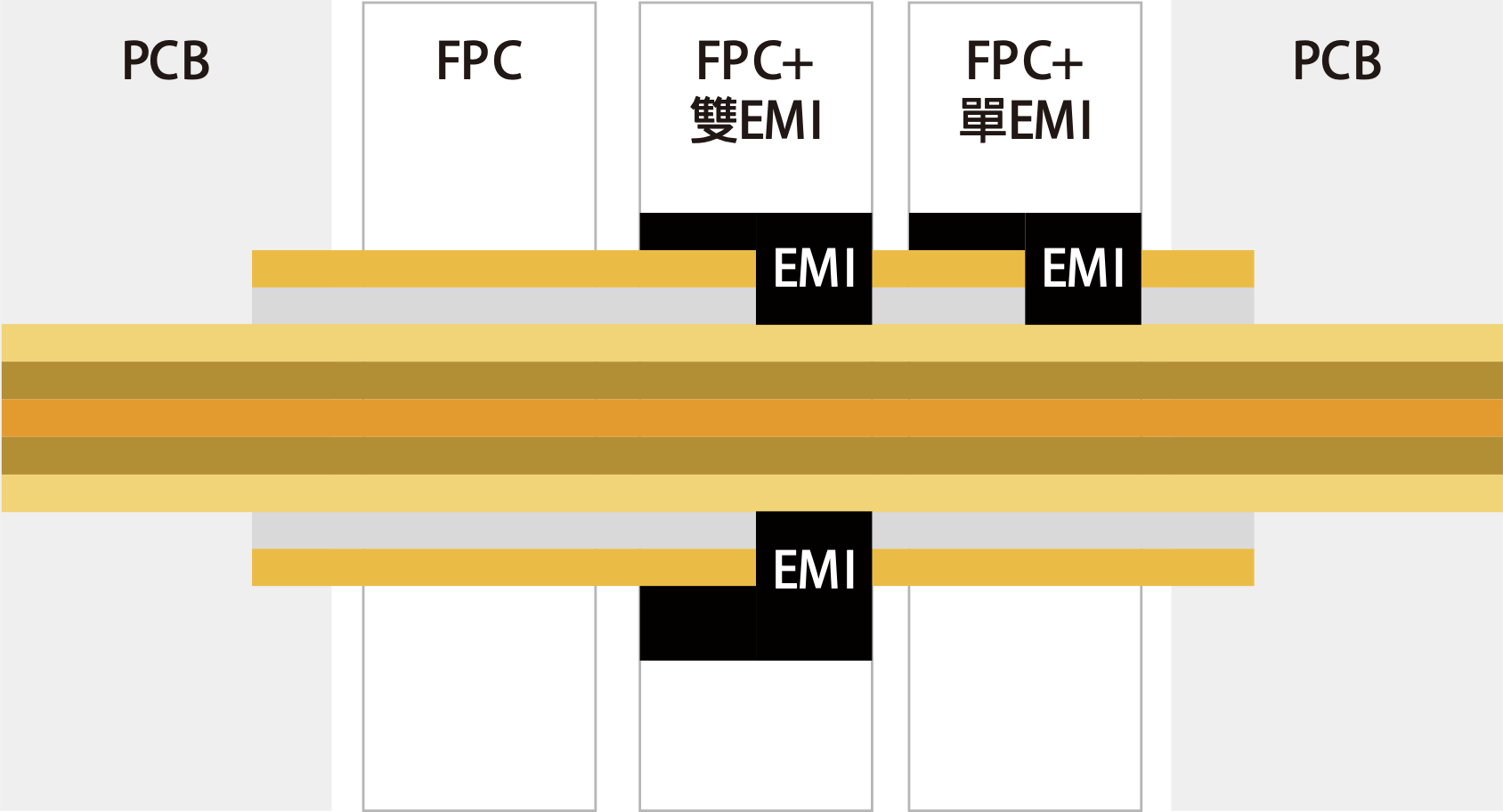
Diagram of Rigid-flex Board Stack Structure with FPC Soft Board Integration.
EMI shielding waves, tape (flat), EMI rubber (3D). The dual EMI shielding effect may result in higher costs.
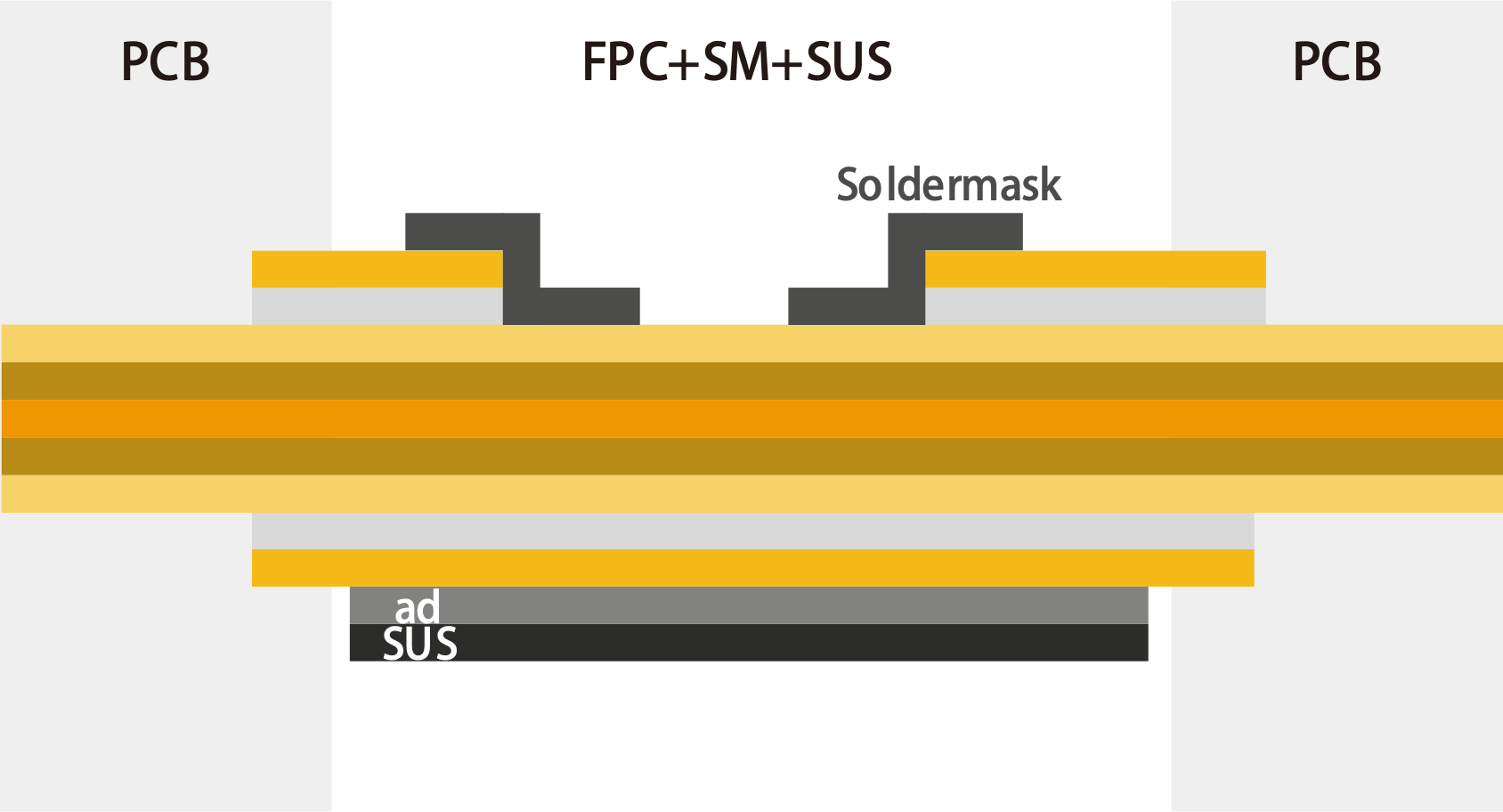
Diagram of Rigid-Flex Board Stack Structure with Solder Mask.
Ad&sus shortens the width, Adhesive (to secure SUS), SUS enhances the flexibility of the soft board.
Traditional Rigid-Flex Board Structure:
The conventional approach to combining rigid and flexible boards typically involves the use of connectors or the HotBar soldering process to connect two rigid boards via a flexible board.
Rigid-Flex Board Structure:
In the case of Rigid-flex boards, the signal is transmitted through a sequence of rigid board → flexible board → rigid board. This configuration shortens the transmission distance, increases speed, and effectively enhances reliability.
The production process of Rigid-flex Boards
Since a Rigid-flex Board is a combination of FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) and PCB (Printed Circuit Board), the production process for Rigid-flex Boards requires equipment for both FPC and PCB manufacturing. Firstly, electronic engineers design the circuit and outline of the flexible board based on requirements. Then, these design specifications are sent to a factory capable of producing Rigid-flex Boards. CAM engineers process and plan the relevant files, and production lines for FPC and PCB are arranged. After the production of these two types of flexible and rigid boards, they are seamlessly laminated using a pressing machine, following the requirements outlined by the electronic engineers. Subsequently, a series of detailed processes is carried out to complete the manufacturing of Rigid-flex Boards.
An essential aspect of this process, given the complexity and numerous details associated with Rigid-flex Boards, is a comprehensive inspection before shipment. Due to their higher value, this step is typically performed to prevent any potential loss of interest for both suppliers and customers.
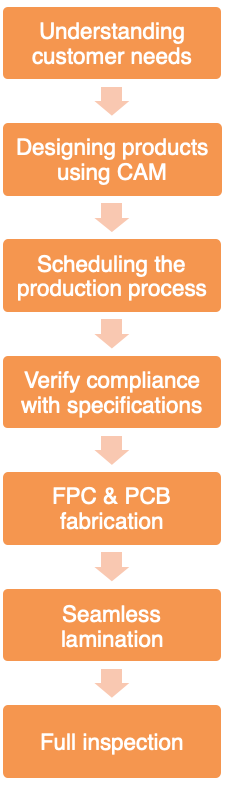
Production Process Flowchart for Rigid-flex Boards.
What are the advantages of using Rigid-flex Boards?
Having explained the design process of Rigid-flex Boards, let's now delve into the advantages of using Rigid-flex Boards:
1.High-impact and high-vibration environments: The flexibility of Rigid-flex Boards allows them to absorb shocks and vibrations, making them suitable for applications that require high durability.
2.Lightweight and enhanced product reliability: The combination of flexible and rigid boards can reduce product weight and shorten signal transmission distances, thereby improving equipment reliability.
3.Precise density and packaging geometric freedom: Flexible printed circuit boards offer packaging flexibility while retaining the precision and repeatability of printed circuits.
4.Mechanical stability: The rigidity of the hard board provides stability, while the flexibility of the soft board allows for more flexible installations within limited spaces and reduces the number of connecting components.
5.Cost reduction and space savings: Compared to conventional PCB wiring processes, process improvements in Rigid-flex Boards can reduce manual assembly and component costs while saving space.
6.Other advantages include flexible design options, high-density circuit boards, excellent heat dissipation, and resistance to chemicals, radiation, and ultraviolet rays.
Products where Rigid-flex Boards can be applied.
Rigid-flex Boards find extensive applications across various fields, particularly with the trend of integrating HDI technology and addressing high-frequency signals, expanding their scope of use. Traditional methods of combining flexible and rigid boards may involve connectors or processes like HotBar soldering to connect two rigid boards via a flexible one.
The application of Rigid-flex Boards offers multiple benefits, including saving circuit board space, eliminating the need for connectors or HotBar soldering, and simplifying the product assembly process. While Rigid-flex Boards come at a higher cost, they are highly versatile, customizable to meet specific requirements, and support high-speed design, making them particularly popular in industrial applications. Apart from military applications, their lightweight characteristics have led to extensive use in products such as aviation and medical equipment.
The following are some real-world applications of Rigid-flex Boards:
1.Mobile phones
2.Laptops
3.Computer tomography (CT) scanners
4.Smart wearable devices
5.Rectifiers
6.ABS detectors
7.Digital cameras
8.Computer servers
9.USB and Ethernet interfaces
10.Barcode scanners
CCP can provide you with Rigid-Flex Boards and a variety of technologies for commercial, high-reliability, or military-grade printed circuit boards. We have also obtained relevant quality certifications, including ISO9001, ISO13485, ISO14001, ISO16949, and QC080000, to ensure product quality.
For further inquiries, please feel free to contact us at https://www.ccpcontactprobes.com/contact.